No ambiente de produção acelerado de hoje, a demanda por processos de produção eficientes e de alta qualidade nunca foi tão grande, particularmente no setor de produtos de limpeza líquidos. Uma linha de produção totalmente automatizada é essencial para atender às expectativas dos consumidores e aos padrões regulatórios. Este artigo explorará os vários componentes dessa linha de produção de shampoo, detalhando suas funções, benefícios, e o impacto geral na fabricação de produtos de limpeza líquidos.
Linha de Produção de Shampoo


1. Manuseio de matérias-primas e Equipamento de mistura
A produção de produtos de limpeza líquidos começa pela matéria-prima, que requerem manuseio cuidadoso e mistura precisa.
- Tanques de armazenamento de ingredientes: Esses tanques são vitais para armazenar matérias-primas líquidas, incluindo surfactantes, solventes, e fragrâncias. Projetado para manter a integridade dos ingredientes, eles geralmente apresentam controles de temperatura e são construídos com materiais resistentes à corrosão. Isso garante que as matérias-primas permaneçam puras e seguras para uso em formulações.
- Tanques de mistura/tanques de agitação: Depois que as matérias-primas são medidas, eles são transferidos para tanques de mistura. Esses tanques são equipados com agitadores potentes que garantem uma mistura completa dos ingredientes. A capacidade de controlar a temperatura através de camisas de aquecimento e resfriamento é crucial, já que muitas reações químicas requerem condições específicas para alcançar resultados ideais.
- Sistemas de pesagem: A precisão é fundamental na formulação de produtos de limpeza. Sistemas de pesagem automatizados permitem a medição de ingredientes em tempo real, reduzindo o erro humano e garantindo que cada lote mantenha a mesma qualidade e características. Este nível de precisão é fundamental tanto para o desempenho quanto para a conformidade regulatória.

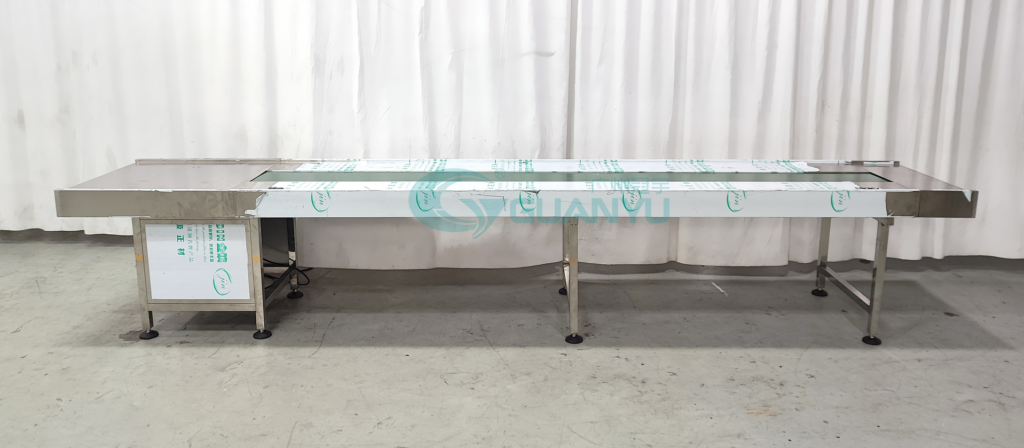
2. Sistemas de Transporte
O transporte eficiente de materiais em toda a linha de produção é essencial para manter o fluxo de trabalho e minimizar o tempo de inatividade.
- Tubulações e Bombas: Estes são essenciais para transferir líquidos misturados para máquinas de envase. A escolha das bombas depende da viscosidade e das propriedades químicas dos produtos, garantindo uma transferência segura e eficaz sem contaminação.
- Correias Transportadoras: Sistemas de transporte automatizados são usados para mover contêineres através de diferentes estágios de produção. Esses sistemas ajudam a reduzir o trabalho manual e aumentam a velocidade das operações, facilitando uma transição perfeita de uma fase para a próxima.

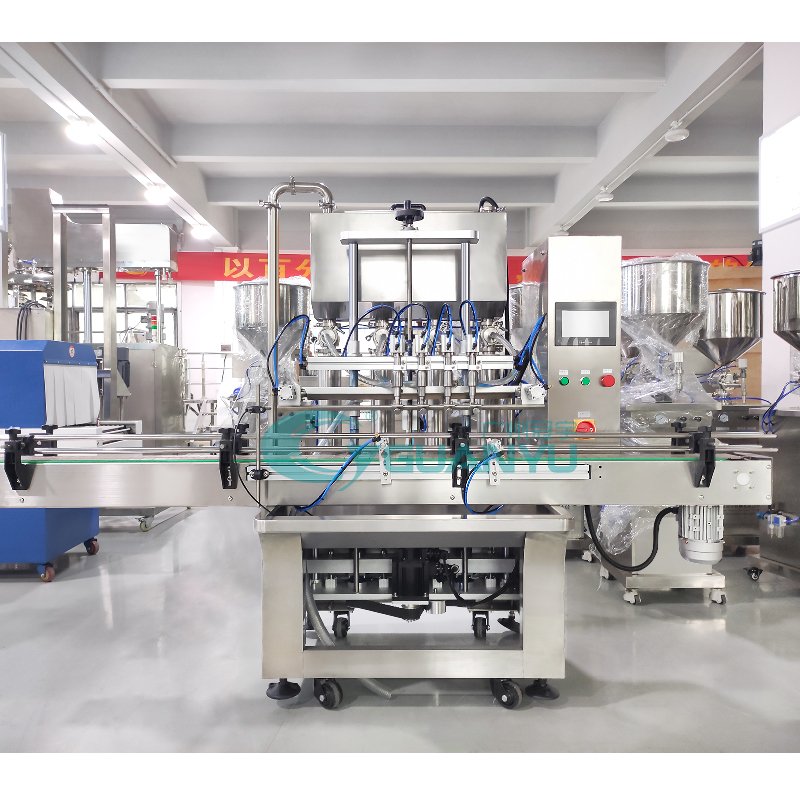
3. Equipamento de enchimento
A fase de enchimento é onde os produtos de limpeza líquidos são embalados em seus recipientes finais.
- Máquinas de enchimento: Dependendo da natureza do líquido, diferentes tipos de máquinas de envase podem ser usados. Por exemplo, enchimentos de bomba de pistão são ideais para produtos viscosos, enquanto as bombas peristálticas são adequadas para formulações mais delicadas. Selecionar o equipamento de enchimento correto é essencial para atingir níveis de enchimento precisos e minimizar o desperdício.
- Sistemas de enchimento com múltiplas cabeças: Para maximizar a eficiência, muitas linhas de produção incorporam sistemas de enchimento com múltiplas cabeças. Estes permitem o enchimento simultâneo de vários recipientes, aumentando significativamente a taxa de produção e reduzindo os tempos de ciclo.

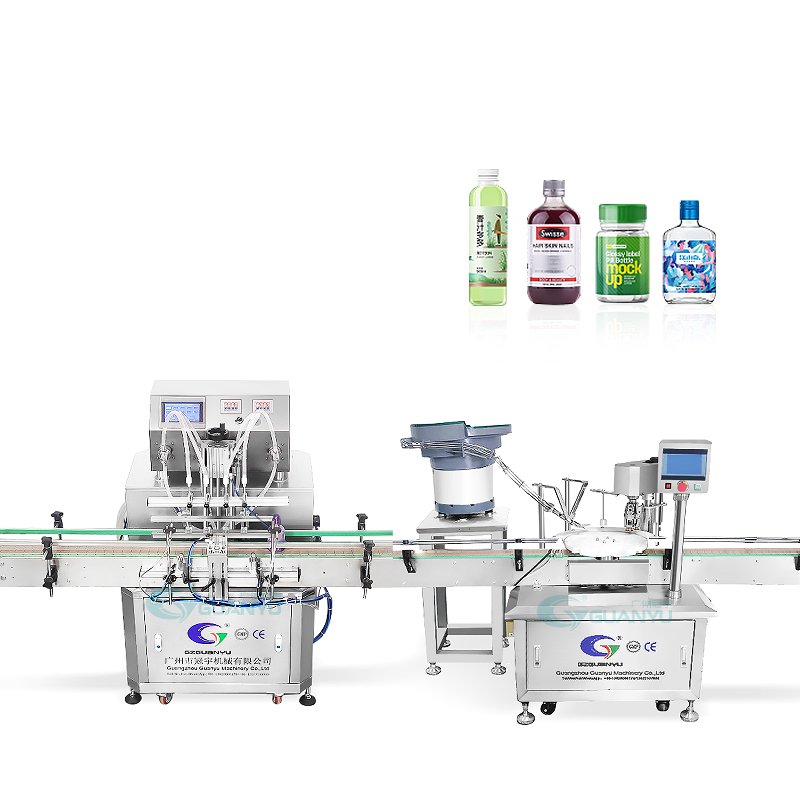
4. Equipamento de vedação
Depois de preencher, é crucial selar as garrafas adequadamente para manter a integridade do produto.
- Máquinas de selagem: Várias tecnologias de vedação, como máquinas de tampar e seladoras de folhas, são utilizados dependendo do tipo de contêiner. Estas máquinas garantem que os produtos permaneçam não contaminados e mantenham a sua qualidade durante todo o seu prazo de validade..
- Classificadores automáticos de tampas: Esses dispositivos agilizam o processo de tampagem, organizando e colocando automaticamente as tampas nas garrafas. Essa automação reduz os custos de mão de obra e aumenta a eficiência operacional.

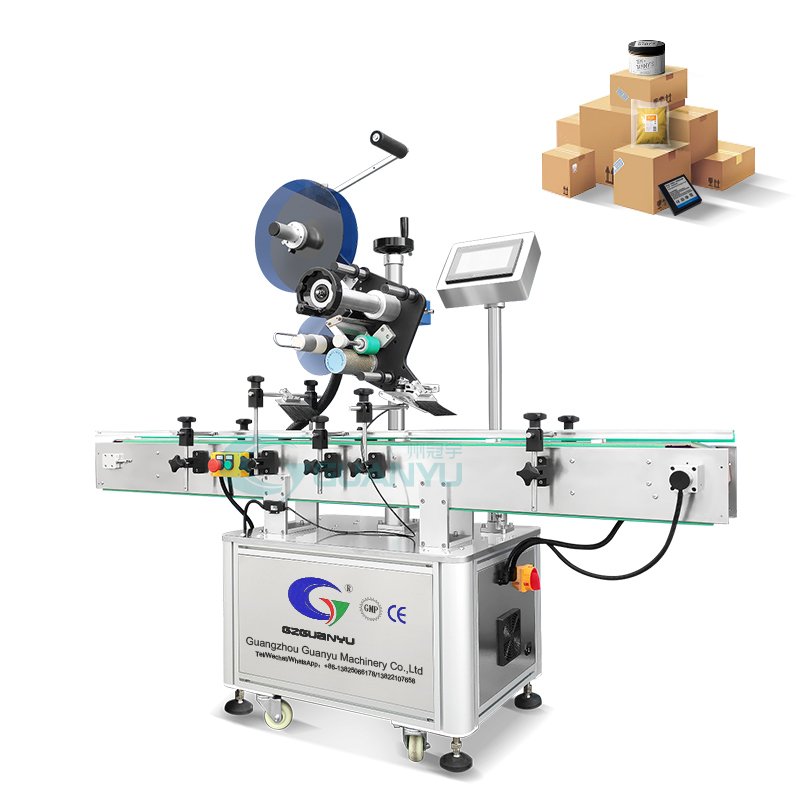
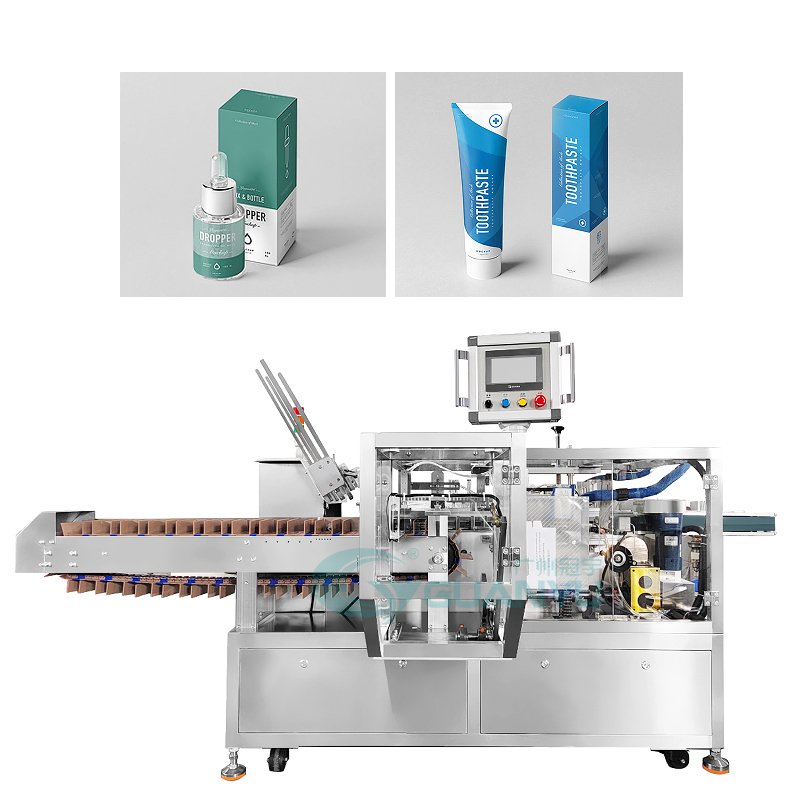
5. Equipamento de etiquetagem e codificação
Rotulagem e codificação eficazes são essenciais para a conformidade e a informação ao consumidor.
- Máquinas de etiquetagem: As etiquetadoras automáticas aplicam etiquetas aos recipientes com eficiência, garantindo posicionamento e aderência precisos. Isto é particularmente importante para requisitos regulatórios e de marca, pois os rótulos devem conter informações específicas.
- Máquinas de codificação/impressoras jato de tinta: Essas máquinas imprimem informações vitais, incluindo números de lote e datas de validade, diretamente no produto. Esta codificação é essencial para a rastreabilidade e conformidade com as normas sanitárias.
6. Equipamento de embalagem
Uma vez que os produtos são selados e rotulados, eles devem ser embalados para distribuição.
- Máquinas de embalagem retrátil: Estas máquinas embrulham garrafas acabadas em filme plástico, fornecendo proteção adicional durante o transporte e melhorando o apelo nas prateleiras. O processo de embalagem retrátil garante que os produtos permaneçam seguros e à prova de violação.
- Máquinas de encadernação: Essas máquinas automatizadas embalam garrafas individuais em caixas, facilitando transporte e armazenamento eficientes. Ao automatizar este processo, os fabricantes podem garantir que os produtos sejam embalados de forma consistente e segura.
- Seladoras de caixas: Finalmente, seladores de caixa são usados para fechar caixas de papelão contendo várias caixas do produto. Esta etapa é essencial para manter a integridade dos produtos durante o transporte e armazenamento.

7. Equipamento de inspeção
O controle de qualidade é um aspecto fundamental do processo de produção.
- Detectores de nível: Esses sistemas monitoram os níveis de líquido em cada garrafa para garantir a conformidade com as especificações. Níveis de enchimento consistentes são vitais para manter a qualidade do produto e a confiança do consumidor.
- Máquinas de verificação de peso: Sistemas automatizados de verificação de peso verificam se cada garrafa cheia atende aos padrões de peso estabelecidos. Esta etapa de controle de qualidade evita perdas financeiras devido a contêineres insuficientemente cheios e garante a conformidade regulatória.
- Sistemas de Inspeção Visual: Sistemas avançados de inspeção usam câmeras para verificar a aparência dos rótulos e a qualidade geral das garrafas. Ao identificar defeitos no início do processo, os fabricantes podem manter padrões de alta qualidade e evitar recalls dispendiosos.
8. Equipamento Auxiliar
Para apoiar a linha de produção, vários sistemas auxiliares são necessários.
- Compressores de ar: Eles fornecem energia pneumática para vários equipamentos de linha de produção, aumentando a eficiência e o desempenho. A manutenção adequada desses sistemas é essencial para a operação contínua.
- CIP (Limpeza no local) Sistemas: A higiene é crucial na fabricação de produtos de limpeza. Os sistemas CIP permitem a limpeza interna dos componentes da linha de produção sem desmontagem, garantindo que todos os equipamentos permaneçam higiênicos e em conformidade com os regulamentos de saúde.
Conclusão
Uma linha de produção totalmente automatizada para produtos de limpeza líquidos é um sistema complexo, mas eficiente, que integra vários equipamentos especializados para garantir a qualidade, velocidade, e segurança durante todo o processo de fabricação. Cada componente, desde o manuseio da matéria-prima até a embalagem final, desempenha um papel vital no fornecimento de produtos de alta qualidade que atendam às expectativas dos consumidores e aos padrões regulatórios.
A integração da automação não só aumenta a produtividade, mas também melhora a consistência e reduz o potencial de erro humano. À medida que o mercado de produtos de limpeza líquidos continua a crescer, os fabricantes que investem em tecnologias de produção avançadas estarão melhor posicionados para atender à crescente demanda, mantendo altos padrões de qualidade e segurança. Ao abraçar a inovação, essas empresas podem prosperar em um cenário competitivo, fornecendo soluções de limpeza eficazes e confiáveis para consumidores em todo o mundo.

Não acho que o título do seu artigo corresponda ao conteúdo haha. Estou brincando, principalmente porque tive algumas dúvidas depois de ler o artigo.
Não acho que o título do seu artigo corresponda ao conteúdo haha. Estou brincando, principalmente porque tive algumas dúvidas depois de ler o artigo.
Você pode ser mais específico sobre o conteúdo do seu artigo? Depois de ler, ainda tenho algumas dúvidas. Espero que você possa me ajudar.
Seu ponto de vista me chamou a atenção e foi muito interessante. Obrigado. Eu tenho uma pergunta para você.
Você pode ser mais específico sobre o conteúdo do seu artigo? Depois de ler, ainda tenho algumas dúvidas. Espero que você possa me ajudar. https://www.binance.info/join?ref=P9L9FQKY
Não acho que o título do seu artigo corresponda ao conteúdo haha. Estou brincando, principalmente porque tive algumas dúvidas depois de ler o artigo.
Seu artigo me ajudou muito, existe mais algum conteúdo relacionado? Obrigado!
Obrigado pela sua partilha. Estou preocupado porque me faltam ideias criativas. É o seu artigo que me deixa cheio de esperança. Obrigado. Mas, Eu tenho uma pergunta, pode me ajudar?
Seu ponto de vista me chamou a atenção e foi muito interessante. Obrigado. Eu tenho uma pergunta para você.
Obrigado pela sua partilha. Estou preocupado porque me faltam ideias criativas. É o seu artigo que me deixa cheio de esperança. Obrigado. Mas, Eu tenho uma pergunta, pode me ajudar?
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom. https://accounts.binance.info/en/register-person?ref=JHQQKNKN
Obrigado pela sua partilha. Estou preocupado porque me faltam ideias criativas. É o seu artigo que me deixa cheio de esperança. Obrigado. Mas, Eu tenho uma pergunta, pode me ajudar?
Seu artigo me ajudou muito, existe mais algum conteúdo relacionado? Obrigado!
Seu ponto de vista me chamou a atenção e foi muito interessante. Obrigado. Eu tenho uma pergunta para você.
Você pode ser mais específico sobre o conteúdo do seu artigo? Depois de ler, ainda tenho algumas dúvidas. Espero que você possa me ajudar.
Você pode ser mais específico sobre o conteúdo do seu artigo? Depois de ler, ainda tenho algumas dúvidas. Espero que você possa me ajudar.
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom.
Seu artigo me ajudou muito, existe mais algum conteúdo relacionado? Obrigado!
Obrigado, seu artigo me surpreendeu, existe um ponto de vista tão excelente. Obrigado por compartilhar, Eu aprendi muito.
Você pode ser mais específico sobre o conteúdo do seu artigo? Depois de ler, ainda tenho algumas dúvidas. Espero que você possa me ajudar.
Obrigado pela sua partilha. Estou preocupado porque me faltam ideias criativas. É o seu artigo que me deixa cheio de esperança. Obrigado. Mas, Eu tenho uma pergunta, pode me ajudar?
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom.
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom.
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom.
Não acho que o título do seu artigo corresponda ao conteúdo haha. Estou brincando, principalmente porque tive algumas dúvidas depois de ler o artigo.
Seu ponto de vista me chamou a atenção e foi muito interessante. Obrigado. Eu tenho uma pergunta para você. https://www.binance.com/id/register?ref=GJY4VW8W
Seu artigo me ajudou muito, existe mais algum conteúdo relacionado? Obrigado!
Seu artigo me ajudou muito, existe mais algum conteúdo relacionado? Obrigado!
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom. Registre-se no binance
Seu ponto de vista me chamou a atenção e foi muito interessante. Obrigado. Eu tenho uma pergunta para você.
Seu ponto de vista me chamou a atenção e foi muito interessante. Obrigado. Eu tenho uma pergunta para você.
Seu ponto de vista me chamou a atenção e foi muito interessante. Obrigado. Eu tenho uma pergunta para você.
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom.
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom.
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom.
Você pode ser mais específico sobre o conteúdo do seu artigo? Depois de ler, ainda tenho algumas dúvidas. Espero que você possa me ajudar.
Você pode ser mais específico sobre o conteúdo do seu artigo? Depois de ler, ainda tenho algumas dúvidas. Espero que você possa me ajudar.
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom. https://accounts.binance.info/en/register-person?ref=JHQQKNKN
Não acho que o título do seu artigo corresponda ao conteúdo haha. Estou brincando, principalmente porque tive algumas dúvidas depois de ler o artigo. https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
Não acho que o título do seu artigo corresponda ao conteúdo haha. Estou brincando, principalmente porque tive algumas dúvidas depois de ler o artigo. https://accounts.binance.info/ES_la/register-person?ref=VDVEQ78S
Obrigado pela sua partilha. Estou preocupado porque me faltam ideias criativas. É o seu artigo que me deixa cheio de esperança. Obrigado. Mas, Eu tenho uma pergunta, pode me ajudar?
Obrigado pela sua partilha. Estou preocupado porque me faltam ideias criativas. É o seu artigo que me deixa cheio de esperança. Obrigado. Mas, Eu tenho uma pergunta, pode me ajudar? https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom.
Jlace2 is a new favorite of mine. Easy to navigate and got some decent odds. Not to bad at all, give it your best shot! jlace2
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom. https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
Seu artigo me ajudou muito, existe mais algum conteúdo relacionado? Obrigado!
Obrigado pela sua partilha. Estou preocupado porque me faltam ideias criativas. É o seu artigo que me deixa cheio de esperança. Obrigado. Mas, Eu tenho uma pergunta, pode me ajudar?
Obrigado por compartilhar. Eu li muitos dos seus posts, legal, seu blog é muito bom.
Seu artigo me ajudou muito, existe mais algum conteúdo relacionado? Obrigado!
**mitolyn**
Mitolyn é um produto cuidadosamente desenvolvido, fórmula à base de plantas criada para ajudar a apoiar a eficiência metabólica e incentivar a saúde, controle de peso duradouro.
Obrigado pela sua partilha. Estou preocupado porque me faltam ideias criativas. É o seu artigo que me deixa cheio de esperança. Obrigado. Mas, Eu tenho uma pergunta, pode me ajudar? https://accounts.binance.com/es/register?ref=RQUR4BEO
Não acho que o título do seu artigo corresponda ao conteúdo haha. Estou brincando, principalmente porque tive algumas dúvidas depois de ler o artigo.